3.5. View Directory Contents with ls
Now that you know how to change directories, it is time to learn how to view the contents of these directories. Using the ls command, you can display the contents of your current directory.
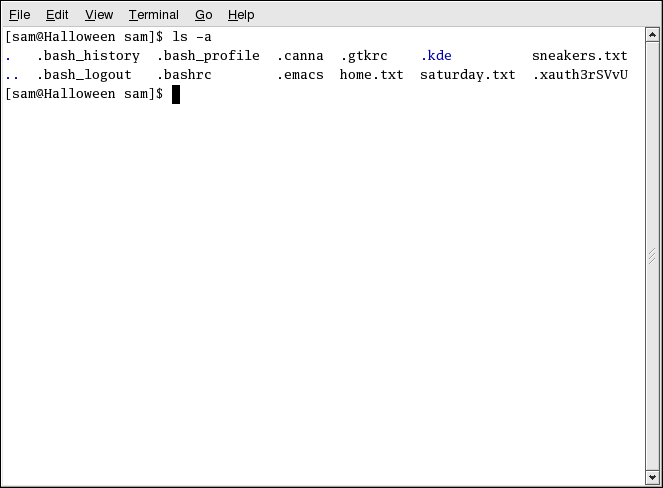
Many options are available with the ls command. The ls command, by itself, does not show all the files in the directory. Some files are hidden files (also called dot files) and can only be seen with an additional option specified to the ls command.
 | Tip |
|---|---|
To view all ls command options, read the man page by typing man ls at a shell prompt. To print the man page, at the prompt type man ls | col -b | lpr. |
Type the command ls -a. Now you can view files that begin with dots.
Hidden files are most often configuration files which set preferences in programs, window managers, shells, and more. The reason they are hidden is to help prevent any accidental tampering by the user. When you are searching for something in a directory, you are not usually looking for these configuration files. Keeping them hidden helps to avoid some screen clutter when viewing directories at the shell prompt.
Viewing all the files using the ls -a command can give you plenty of detail, but you can view still more information by using multiple options.
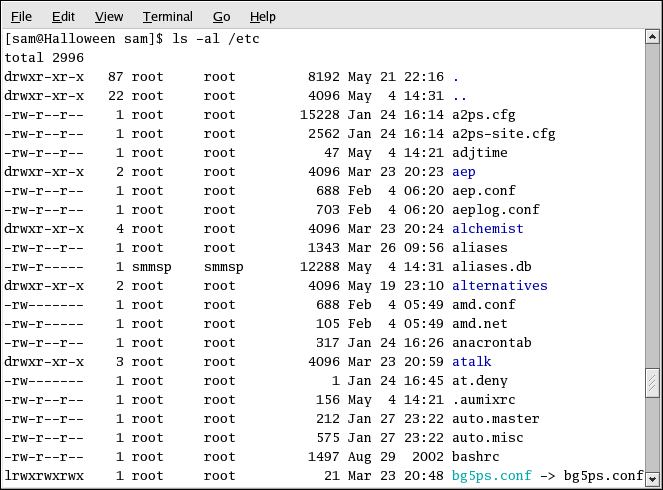
If you want to see the size of a file or directory, when it was created, and so on, add the long option (-l) to the ls -a command. This command shows the file creation date, its size, ownership, permissions, and more.
You do not have to be in the directory whose contents you want to view to use the ls command. For example, to see what is in the /etc/ directory from your home directory, type:
ls -al /etc |
The following is a brief list of options commonly used with ls. Remember, you can view the full list by reading the ls man page (man ls).
-a (all) — Lists all files in the directory, including hidden files (.filename). The .. and . at the top of your list refer to the parent directory and the current directory, respectively.
-l (long) — Lists details about contents, including permissions (modes), owner, group, size, creation date, whether the file is a link to somewhere else on the system and where its link points.
-F (file type) — Adds a symbol to the end of each listing. These symbols include /, to indicate a directory; @, to indicate a symbolic link to another file; and *, to indicate an executable file.
-r (reverse) — Lists the contents of the directory in reverse sort order.
-R (recursive) — Lists the contents of all directories below the current directory recursively.
-S (size) — Sorts files by their sizes.